Menstrual Health and Irregularities
Menstrual health and irregularities are key indicators of women’s reproductive and hormonal health. Consistent menstrual cycles suggest a healthy body, while changes in cycle length, flow, or frequency may signal underlying health conditions. Understanding what’s normal—and what isn’t—helps you take timely action and seek appropriate care.
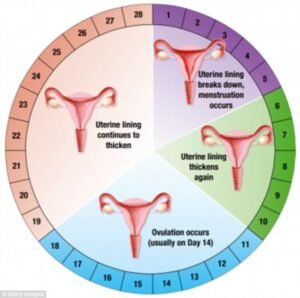
What Is Menstrual Health?
Menstrual health refers to:
- Regular, predictable menstrual cycles
- Manageable flow and duration
- Minimal discomfort that doesn’t disrupt daily life
A healthy menstrual cycle is defined by a 21–35-day interval and a menstrual flow lasting 3–7 days.
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle
Normal signs include:
- Consistent cycle length
- Moderate bleeding
- Mild cramps
Irregularities may include:
- Missed or delayed periods
- Heavy or very light bleeding
- Spotting between cycles
- Severe pain or fatigue
Common Causes of Menstrual Irregularities
- Hormonal imbalances (thyroid issues, PCOS)
- Lifestyle factors (stress, weight changes, excessive exercise)
- Medical conditions (fibroids, endometriosis)
- Age-related changes (adolescence, perimenopause)
When Should You Seek Help?
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Periods absent for 3 months or more
- Excessive bleeding or clots
- Severe pain affecting daily activities
- Sudden, unexplained cycle changes
Why Early Care Matters
Timely evaluation can:
- Prevent complications
- Improve fertility outcomes
- Enhance overall quality of life
Cycle tracking and awareness of menstrual changes empower individuals to protect and maintain Menstrual Health and Irregularities
Overview of Menstrual Health
What does menstrual health mean?
Menstrual health and irregularities encompass the normal regulation of the menstrual cycle, including cycle regularity, adequate menstrual flow, minimal pain, and emotional stability, reflecting balanced hormonal activity and healthy reproductive function.
Why regular cycles matter for overall health
Regular menstrual cycles are a sign of balanced hormones and a healthy reproductive system. Consistent cycles are often linked to:
- Normal ovulation and fertility
- Stable hormonal levels
- Good nutritional and metabolic health
Changes in cycle regularity may be a sign of stress, hormonal disorders, or other medical issues that should be evaluated.
Menstruation as a vital health sign
A woman’s menstrual health and irregularities act as a monthly health check for the body. Irregularities in cycle length, flow, or symptoms may indicate hormonal imbalance, thyroid disorders, or reproductive health problems. Monitoring menstrual patterns enables early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention.
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
What Is a Normal Menstrual Cycle?
A normal menstrual cycle is a sign of stable hormonal activity and well-functioning reproductive organs. Key features include:
- Most women have a menstrual cycle that lasts about 21 to 35 days.
- Bleeding duration: Usually lasts 3 to 7 days
- Normal flow characteristics:
- Moderate bleeding that does not soak pads or tampons excessively
- Healthy menstrual blood color varies from bright red to dark brown.
- Mild cramps that do not interfere significantly with daily activities
Slight variations in the menstrual cycle may occur from month to month, particularly during adolescence or times of physical or emotional stress.
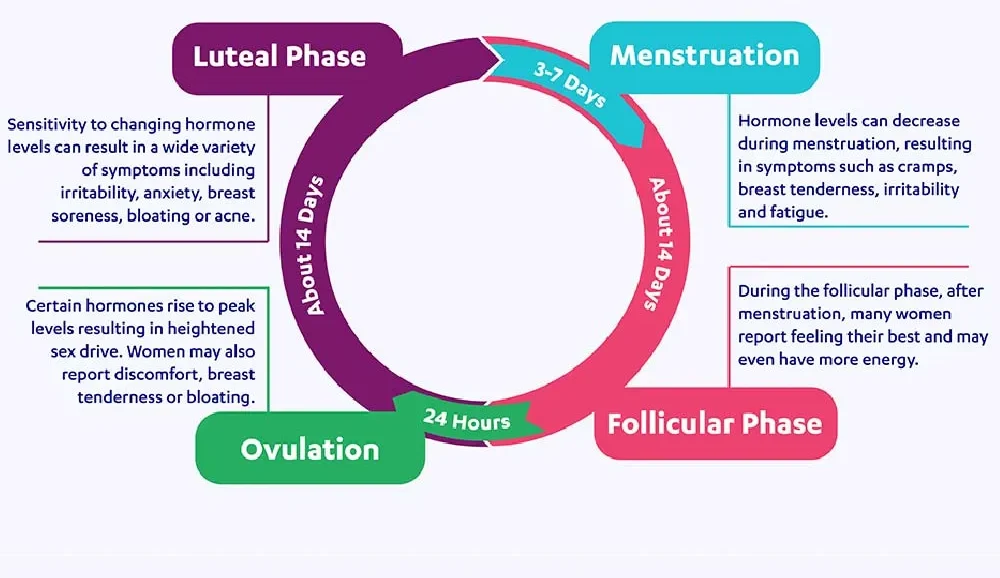
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle includes four main stages, driven by hormonal changes in the body.
1. Menstrual phase
- Shedding of the uterine lining
- Bleeding occurs for a few days
2. Follicular phase
- Hormones stimulate egg development in the ovaries
- The uterine lining begins to rebuild
3. Ovulation
- Release of a mature egg from the ovary
- This is the most fertile phase of the cycle
4. Luteal phase
- Hormones prepare the uterus for possible pregnancy
- If pregnancy does not occur, hormonal levels decline, starting the next menstrual period.
Common Types of Menstrual Irregularities
Irregular cycles: Menstrual cycles occur at irregular intervals each month.
Missed periods (amenorrhea): The absence of menstruation for one or more cycles, not related to pregnancy.
Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia): Excessive menstrual flow that lasts longer than usual or requires frequent changes of pads or tampons.
Painful periods (dysmenorrhea): Menstrual cramps or pelvic pain intense enough to disrupt daily activities and reduce quality of life.
Frequent periods (polymenorrhea): Frequent menstrual cycles occurring in less than 21-day intervals.
Understanding the specific type of menstrual irregularity helps healthcare providers identify possible causes and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Normal vs Abnormal Periods
| Feature | Normal Periods | Irregular Periods |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle length | 21–35 days | Less than 21 days or more than 35 days |
| Flow | Moderate, manageable | Very heavy or very light |
| Duration | 3–7 days | Less than 2 days or more than 7 days |
| Pain | Mild, does not limit activities | Severe or disabling pain |
Symptoms of Menstrual Irregularities
Common Symptoms
Women with menstrual health and Irregularities: You may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Delayed or missed periods
- Excessive menstrual bleeding
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Severe menstrual cramps or pelvic pain
- Fatigue, weakness, or dizziness during or around periods
Other Associated Symptoms
Menstrual irregularities may be accompanied by symptoms of hormonal imbalance, including:
- Acne or sudden skin changes
- Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
- Excess facial or body hair growth, or hair thinning
- Mood swings, irritability, or emotional changes
Early recognition of these symptoms helps in seeking timely medical care and proper treatment.
Causes of Irregular Periods
Common Symptoms
Several medical conditions can disrupt normal hormonal function and affect the regularity of the menstrual cycle, including:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
A common hormonal condition that interferes with ovulation and leads to irregular or missed periods.
Thyroid disorders
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can alter menstrual timing, flow, and cycle regularity.
Hormonal imbalances
Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can impact cycle length, bleeding patterns, and overall menstrual health.
Uterine fibroids
Benign growths in the uterus that may cause heavy bleeding, prolonged periods, or irregular menstrual cycles.
Endometriosis—A condition where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus, leading to pain and irregular periods
Lifestyle Factors
Daily habits and lifestyle choices can significantly impact menstrual regularity, such as:
- Stress—Emotional or physical stress can delay or skip ovulation
- Sudden weight loss or gain—Rapid changes in body weight affect hormone production
- Excessive exercise—Intense physical activity may suppress normal menstrual function
- Poor nutrition—Deficiencies in essential nutrients can disrupt hormonal balance
Age-Related Causes
Hormonal changes at certain life stages can naturally affect menstrual cycles:
- Adolescence – Irregular cycles are common in the first few years after the first period
- Perimenopause—Fluctuating hormone levels before menopause often cause cycle changes
Understanding the underlying cause is essential for proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
Diagnosis of Menstrual Irregularities
How Doctors Diagnose the Problem
To identify the cause of menstrual irregularities, healthcare providers use a step-by-step evaluation that may include:
Menstrual history: Review of cycle length, flow pattern, missed periods, pain, and related symptoms.
Physical examination: General and pelvic examination to check for signs of hormonal or gynecological conditions.
Blood tests: Tests to assess hormone levels, thyroid function, and other relevant health indicators.
Ultrasound scan: Imaging to evaluate the uterus and ovaries for fibroids, cysts, or structural abnormalities.
Hormonal evaluation: Detailed assessment of reproductive hormones to detect imbalances affecting the menstrual cycle.
Accurate diagnosis helps in planning the most effective and personalized treatment.
Treatment Options for Irregular Periods
Medical Management
Medical treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms and may include:
Hormonal therapy
Used to regulate menstrual cycles and correct hormonal imbalances.
Cycle-regulating medicines
Medications that help restore regular timing and reduce abnormal bleeding.
Pain management
Medicines to relieve menstrual cramps and pelvic discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy lifestyle changes play a key role in improving menstrual regularity:
Balanced diet: Adequate intake of nutrients supports hormonal balance.
Stress management: Relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or counseling can help regulate cycles.
Regular exercise: Moderate physical activity promotes overall reproductive and metabolic health.
Surgical Options
Surgical treatment is considered when medications and lifestyle changes are not effective:
Fibroid removal: Surgery to remove uterine fibroids causing heavy or irregular bleeding.
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure commonly used in the management of endometriosis.
Hysteroscopy: A procedure to examine and treat abnormalities inside the uterus.
Treatment should always be personalized based on medical evaluation and patient needs.
Natural Ways to Support Menstrual Health
Medical Management
Simple daily habits can help maintain hormonal balance and promote regular menstrual cycles:
Regular sleep: Maintaining consistent sleep patterns supports hormone regulation and overall reproductive health.
Iron-rich foods: Including foods like green leafy vegetables, legumes, and dates helps prevent anemia, especially during heavy periods.
Hydration: Drinking enough water reduces fatigue and bloating and helps maintain healthy circulation during menstruation.
Yoga and meditation: Gentle yoga poses and mindfulness practices help reduce stress, improve blood flow, and support cycle regularity.
These natural measures can complement medical care and contribute to long-term Menstrual Health and Irregularities.
Menstrual Health in Adolescents
What Is Normal After Menarche?
After menarche (the first menstrual period), it is common for adolescents to experience changes as the body adjusts hormonally:
Irregular cycles in the first 1–2 years
Menstrual cycles may be unpredictable in timing and flow as the hormonal system matures. This is usually normal and improves over time.
When parents should worry
Medical advice should be sought if there are:
- Periods absent for more than 3 months
- Very heavy bleeding or severe pain
- Periods lasting longer than 7 days
- Signs of anemia, extreme fatigue, or sudden weight changes
Early guidance and reassurance help adolescents develop healthy menstrual habits and prevent future complications.
Menstrual Health and Fertility
How do irregular cycles affect ovulation?
Irregular menstrual cycles often indicate irregular or absent ovulation. When ovulation does not occur regularly, predicting fertile days becomes difficult, which can reduce the chances of conception. Hormonal imbalances, PCOS, and thyroid disorders commonly link menstrual irregularities with fertility challenges.
When to seek fertility evaluation?
Fertility evaluation is recommended if:
- Periods are consistently irregular or absent
- Pregnancy does not occur after 12 months of regular unprotected intercourse (or 6 months if the woman is over 35 years)
- There are known hormonal or gynecological conditions affecting cycles
Early assessment helps identify treatable causes and improves the likelihood of successful conception.
Case Studies
Case Study 1 – Young Woman with PCOS
Symptoms
Irregular periods, weight gain, acne, and increased facial hair growth.
Diagnosis
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) was confirmed through hormonal evaluation and pelvic ultrasound.
Treatment outcome
With hormonal therapy, dietary changes, and regular exercise, menstrual cycles became more regular and symptoms gradually improved.
Case Study 2 – Stress-Induced Irregular Periods
Lifestyle correction
The patient adopted stress-management techniques, improved sleep habits, and followed a balanced diet.
Cycle normalization
Within a few months, menstrual cycles returned to a regular pattern without the need for medication.
These examples highlight how identifying the root cause leads to effective and personalized treatment.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Warning Signs
Seek medical advice if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Heavy bleeding that requires frequent pad or tampon changes or lasts longer than normal
- Missed periods for 3 months or more without pregnancy
- Severe pain during periods that interferes with daily activities
- Sudden cycle changes in timing, flow, or intensity without an obvious cause
Early consultation helps in identifying underlying conditions and ensures timely and effective treatment.
Prevention Tips
Simple preventive measures can help maintain regular and healthy menstrual cycles:
Track menstrual cycles
Keeping a record of cycle dates, flow, and symptoms helps identify early changes and patterns.
Maintain a healthy weight
Balanced nutrition and regular physical activity support hormonal balance and cycle regularity.
Regular health checkups
Periodic medical visits allow early detection and management of hormonal or gynecological issues.
Consistent preventive care plays an important role in long-term menstrual health and irregularities.
Conclusion
Menstrual Health and Irregularities is a vital reflection of overall physical and hormonal well-being. Paying attention to changes in the menstrual cycle can provide early clues to underlying health concerns. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications, while timely and appropriate medical care supports better reproductive health, improved comfort, and a higher quality of life.
FAQs
Is it normal to miss periods occasionally?
Yes, occasionally missing a period can be normal and may happen due to stress, illness, travel, or sudden lifestyle changes. However, if missed periods occur frequently or for a prolonged duration, it is important to seek medical evaluation to rule out underlying causes.
How many days’ delay in periods is considered normal?
A delay of about two to seven days is generally considered normal. Delays beyond this range, especially if they happen regularly, may suggest hormonal imbalance or other health-related issues.
When should I see a gynecologist for irregular periods?
You should see a gynecologist if your periods are missed for three months or more, if you experience very heavy or prolonged bleeding, if menstrual pain is severe enough to interfere with daily activities, or if there are sudden and unexplained changes in your menstrual cycle pattern.
Can stress cause irregular periods?
Yes, both physical and emotional stress can disturb hormonal balance in the body. This may delay ovulation or temporarily stop periods, resulting in irregular menstrual cycles.
Do irregular periods affect pregnancy?
Irregular periods can make ovulation unpredictable, which may reduce the chances of conception. However, with proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many women with irregular cycles are able to conceive successfully.
Are irregular periods common in teenagers?
Yes, irregular menstrual cycles are common during the first one to two years after the first period, as the body is still adjusting hormonally. If irregularity continues beyond this period or is associated with heavy bleeding or severe pain, medical advice should be sought.
Can weight changes affect menstrual cycles?
Yes, sudden weight gain or weight loss can disrupt hormone levels in the body. These hormonal changes can lead to delayed, missed, or irregular periods.
Are painful periods always a cause for concern?
Mild menstrual cramps are common and usually normal. However, severe or worsening pain may indicate conditions such as endometriosis or fibroids and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Can lifestyle changes improve irregular periods?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve overall menstrual health and irregularities.
Should I track my menstrual cycle?
Yes, tracking your menstrual cycle helps you understand what is normal for your body, identify irregular patterns early, and provides valuable information when consulting a healthcare professional.
